What is colorectal cancer?
Incidence1
- • CRC is the third most incident cancer
- •Almost 1.9 million new cancer cases are expected to be diagnosed in 2020
Mortality1
- • CRC is the third leading cause of cancer death
- •Almost 935,173 deaths/year
Risk2,3,4
- • The risk of CRC increases significantly after the age of 50
How does colorectal cancer develop?
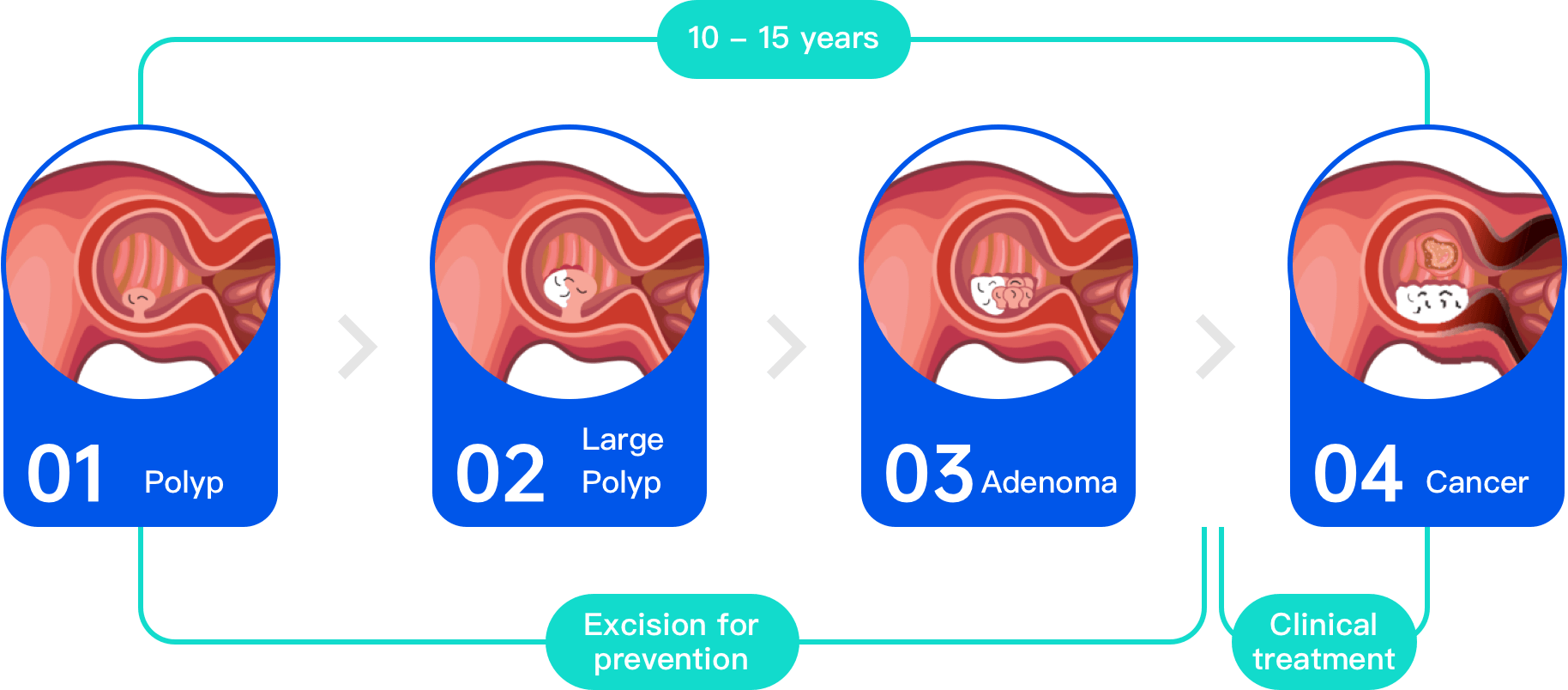
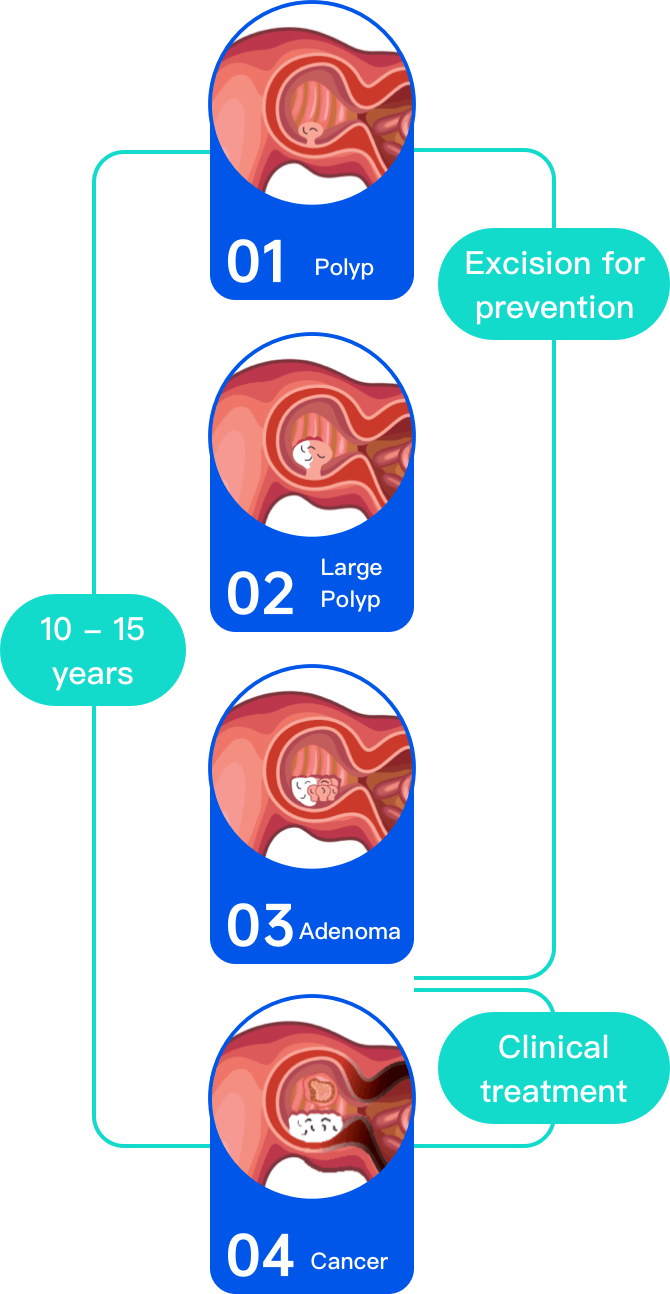
Why colorectal cancer is hard to be detected in early stages?
Colorectal cancer is increasing in younger adults year by year. But it does not usually produce symptoms in the early stages of disease. If colorectal cancer is caught in early stages, it is more treatable.
As the tumor grows, patients may experience one or multiple symptoms.These may include the following:
Blood in the Stool、Rectal Bleeding、Changes in Bowel Habits、Abdominal Pain and Bloating、Nausea and Vomiting、Anemia、Unexplained Weight Loss, Loss of Appetite and Feeling Weak and Pelvic Pain.5
Tests for colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis include the following:fecal occult blood test, barium enema, flexible sigmoidoscopy,colonoscopy, virtual colonoscopy, and stool DNA test.5
What Are the Risk Factors for Colorectal Cancer2
Colorectal cancer risk factors you can change6
- • Being overweight or obese
- •Not being physically active
- •Certain types of diets
- •Smoking
- •Alcohol use
Colorectal cancer risk factors you cannot change:
- • Being older
- •A personal history of colorectal polyps or colorectal cancer
- •A personal history of inflammatory bowel disease
- •A family history of colorectal cancer or adenomatous polyps
- •Having an inherited syndrome
- •Your racial and ethnic background
- •Having type 2 diabetes

What kind of screening options available?
Colonoscopy (Golden standard)
Repeat every 10 years, if negative
- • Golden standard
- •High sensitivity for colorectal cancer
- •Lesions can be removed at time of detection

Fecal immunochemical test (FIT)
Repeat every 1-3 years, if negative
- • Non-invasive
- •Low cost

Stool DNA test
Repeat every 3 years, if negative
- • High sensitivity for colorectal cancer and advanced precancerous lesions
- •Non-invasive
- •Self-sampling at home
- •No special preparation required
References:
- 1.The data presented here comes from the Global Cancer Observatory, owned by the World Health Organization/International Agency for Research on Cancer (last accessed 17 August 2022).
- 2.Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238.ssaa
- 3.Adult Screening Programme, Bowel Cancer. UK NSC screening recommendation. Accessed August 22, 2022. https://view-health-screening-recommendations.service.gov.uk/bowel-cancer/
- 4.Evidenced-based Guideline for Colorectal Cancer. Version 2.1 – January 2019 AWMF-Registration Number: 021/007OL. German Guideline Program in Oncology (GGPO). Accessed August 22, 2022. https://www.leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Leitlinien/Kolorektales_Karzinom/Version_2/GGPO_Guideline_Colorectal_Cancer_2.1.pdf
- 5.https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/colon-cancer
- 6.https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
Intended Use and Important Risk Information:
The Combined Detection Kit for Human Gene Methylation and Fecal Occult Blood is a non-invasive in vitro diagnostic (IVD) assay for qualitative detection of certain genes’ methylation and fecal hemoglobin from human stool specimens. The kit is intended to be used for screening colorectal cancer in the general population. A positive test result indicates that the subject may have colorectal cancer and/or advanced adenoma, and further colonoscopy is required; on the contrary, a negative test result indicates that the subject has a low possibility of colorectal cancer and/or advanced adenoma, however, the risk of disease cannot be completely ruled out. The product is applicable to all people between the ages of 40 to 75 who need colorectal cancer screening.
This product cannot replace colonoscopy, and the test results of this kit should not be used as the only basis for clinical diagnosis. Clinicians should comprehensively judge the results based on the patient's condition and other laboratory indicators. CE marked.
